How to use Vercel Edge Config in your Functions

Photo by Fiona Smallwood on Unsplash
I recently had to chance to use Vercel Edge Config for a project where I needed to manage a small amount of key-value data and didn’t want to go down the path of setting up database infrastructure to manage it. If you’re like me and haven’t heard about Edge Config, its “a key-value data store (…) [that] enables you to read data at the edge without querying an external database”.
This comes in useful for things such as setting up feature flags without requiring a redeployment, A/B testing or, in my case, managing API authorisation tokens. You can find out more about my particular use case in my previous post on Tracking progress on my 2023 goals.
Before I get into how to use Edge Config, there are some important things that are important to know:
- The store is associated with your Vercel account as opposed to a particular project. This means you can share Edge Config between multiple projects or manage access on a project-by-project basis.
- Edge Config is very small. Plan limits range from 8 KB of storage for Hobby accounts to 512 KB for Enterprise
- It should only be used for data that is read frequently and written to infrequently. This is because write operations can take up to 10 seconds to propagate globally so there is no guarantee of consistent reads.
- As of writing, the feature is currently in beta.
Getting Started
To get started with Vercel Edge Config, you first need to enable Edge Config on your account by logging into your Vercel account and going to the “Edge Config” tab. From there it will prompt you to create your first store.
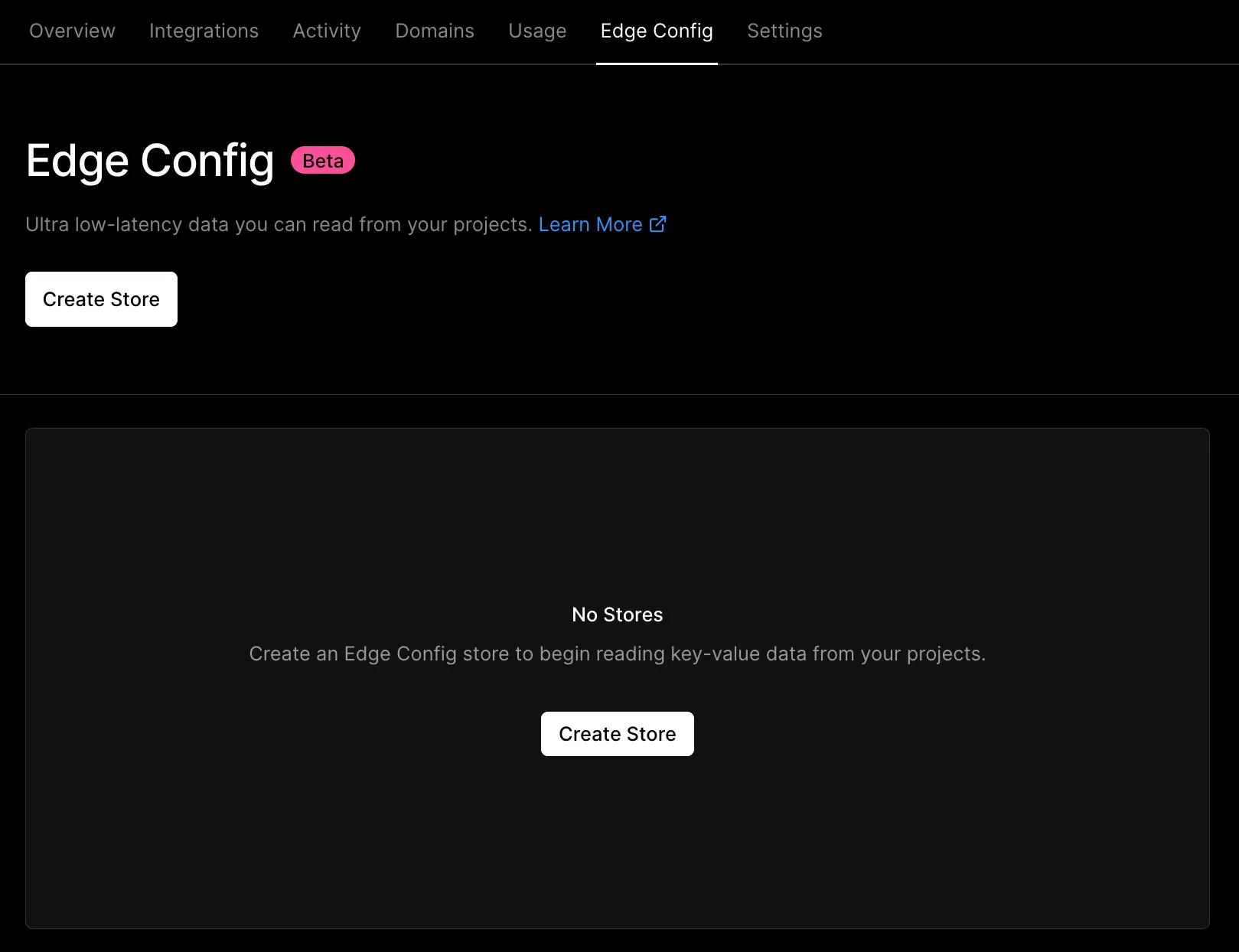
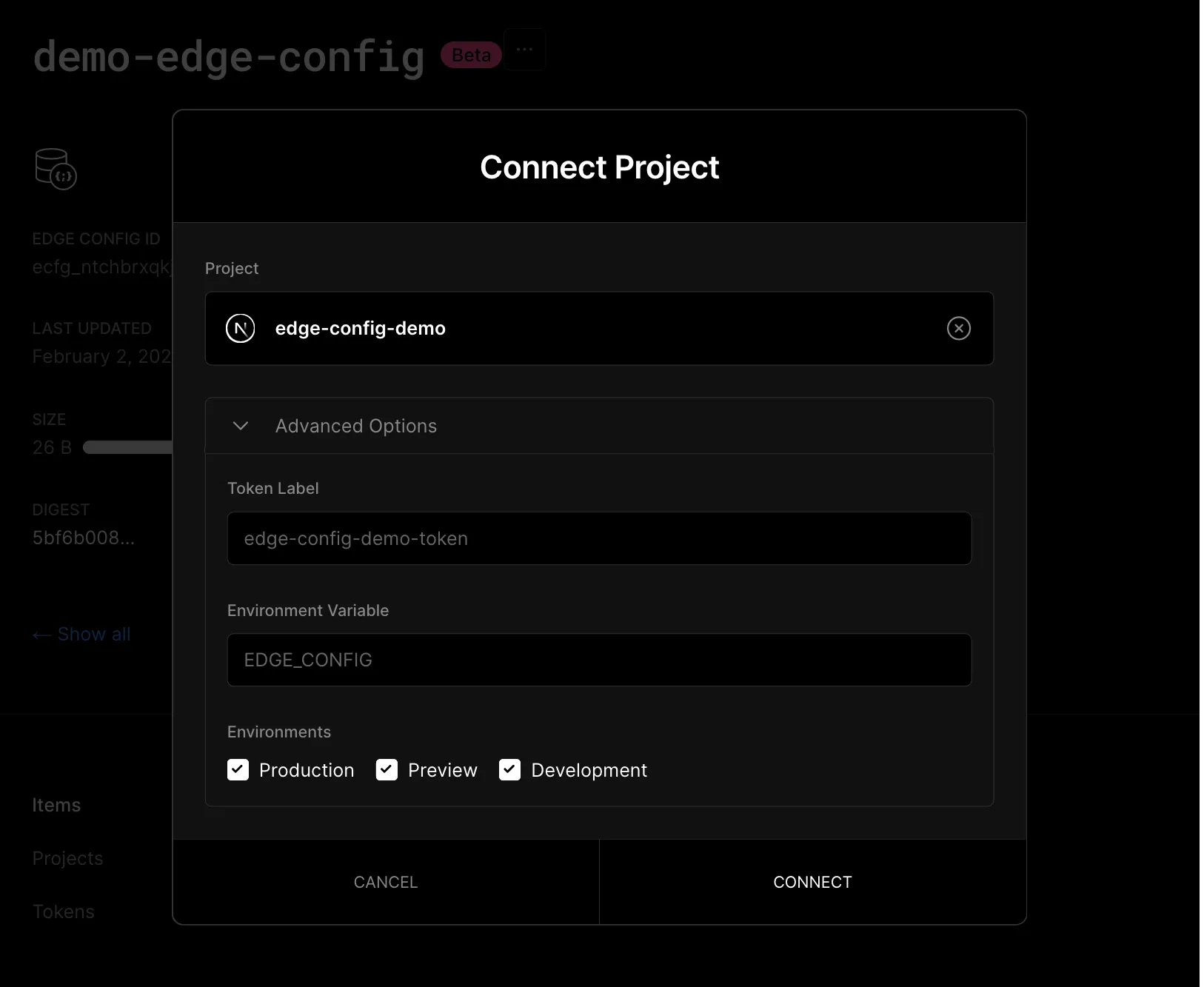
On creation, it will give you an example key-value pair which we are going to use for the rest of this article. Next, you will need to connect your project to the store. This can be done in the “Projects” menu. When you connect your project to the store, it will set the EDGE_CONFIG environment variable which is a token that is used to authenticate with your Edge Config.
Reading from Edge Config
Reading from Edge Config is fairly easy if you’re also using Vercel Functions. First, you will need to install @vercel/edge-config as a dependency in your project.
Then its just a case of using the getAll function passing in a list of variables you would like to receive. If you omit the list, it will return all variables in the Edge Config. The @vercel/edge-config package makes use of the EDGE_CONFIG environment variable we created in the previous step so if you’re having issues authenticating, that is the first place to look.
import { getAll } from "@vercel/edge-config";
const { greeting } = await getAll(["greeting"]);Writing to Edge Config
The easiest way to update the Edge Config is through the Vercel Dashboard however you’ll often need to update it through your Vercel Functions. The easiest way to do this is to make a PATCH request to your Edge Config URL which will look something like this:
https://api.vercel.com/v1/edge-config/your_edge_config_id_here/itemsThe body of your request should be a list of items which include:
operation- eithercreate,update,deleteorupsertwhich creates the item if it doesn’t exist and updates it if it doeskey- the key of the item you want to perform the operation onvalue- the value of the item which can only be astring,number,object,nullor an array of the previous types
To make the request, you will also need to create a Vercel API Access Token using these instructions and add it to your project environment variables as VERCEL_ACCESS_TOKEN (or any other descriptive name) so we can use it in the request headers. Note that if when you update your project environment variables, they won’t take effect until you redeploy your app.
Another important thing to note is that you must also specify 'content-type': 'application/json' in your headers or you’ll get an error message saying "Unsupported Media Type".
Upon making the request; you can check the status parameter in the result to see if all the operations you performed were successful as shown in the following example.
const result = await fetch(
"https://api.vercel.com/v1/edge-config/your_edge_config_id_here/items",
{
method: "PATCH",
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.VERCEL_ACCESS_TOKEN}`,
"content-type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
items: [
{
operation: "update",
key: "greeting",
value: "hello vercel",
},
],
}),
}
);
const json = await result.json();
if (json.status !== "ok") {
console.error("Failed to update edge config", json);
}If you’re already using Vercel to host your site, I’d highly recommend giving Edge Config a try if you need a small amount of key-value storage without having to set up your own database infrastructure.